

A patient with hip pain after a fall whose xrays are (apparently) negative needs admission to the hospital and an MRI.Īs noted, medical co- morbidities can be expected. Occult fractures are rare but not impossible. An isolated fracture of the greater trochanter may occur as an avulsion by the gluteus medius, and needs only symptomatic (palliative) treatment DiagnosisĬare must be taken to rule out the more benign isolated fracture of the greater trochanter an MRI or CT may be needed for that purpose.

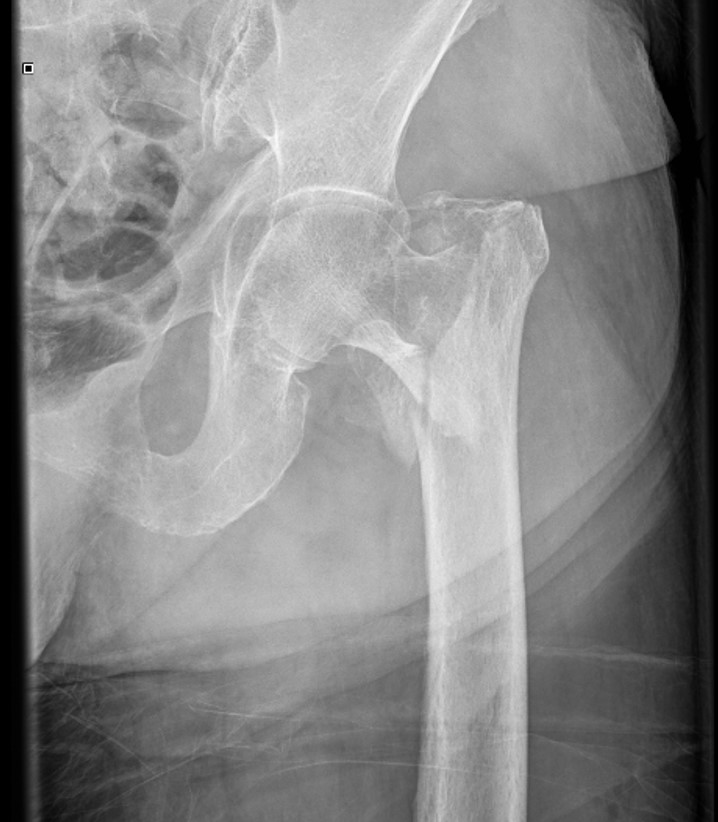
Patients with hip fractures are typically sick, but they were sick in the moments preceding the fracture as well, in all likelihood. This is not so much an academic debate about causality but a warning to clinicians to expect -and seek, if not initially found?medical co-morbidities. This gives rise to the conjecture that poor soft tissue padding, poor reflexes and weakness are actually what causes the fracture. Although the kinetic energy of such a fall is far more than is needed to break the bone, most falls do not lead to fracture. Intertrochanteric fractures are often seen in frail older people after low energy falls (ie, from a standing height). The key criterion of any robust classification is whether the fracture can be considered stable or unstable. Even if there is no comminution and even if the fracture line does not reach the subtrochanteric region, this fracture is unstable and prone to displacement with conventional sliding screws, as the fracture line is parallel to the course of the sliding screw and displaces as the screw slides. In reverse obliquity fractures, the fracture line courses laterally as it extends from proximal to distal, running perpendicular to the intertrochanteric line. IV displaced with lesser trochanteric (posteromedial) andĪ special category is the "reverse obliquity fracture". III displaced with greater trochanteric (posterolateral) comminution Intertrochanteric fractures can be classified (Evans, 1949) as the following Types: The adductors attach to the shaft below the intertrochanteric region, possibly displacing the shaft medial relative to the proximal fragment(s). The abductors and short external rotators attach to the greater trochanter the iliopsoas to the lesser. AnatomyĪs the name implies, an intertrochanteric fracture is one where the fracture line lies between the greater and lesser trochanters. Unlike a subtrochanteric fracture, it can be (but not always is) inherently stable. Unlike a femoral neck fracture, the intertrochanteric region has good blood supply to cancellous bone, and thus has good healing potential. See Hip fractures for a general discussion. Our experience demonstrated that this surgical technique reduced the intraoperative risk for patients.Hip fractures can be divided into two groups: intra-capsular femoral neck fractures (further localized as subcapital, transcervical or basicervical) and extra-capsular peri-trochanteric fractures, namely the intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures.
After that, the rod of nail was pulled back a little to make the wire in the middle of the tack hole, which can facilitate the insertion of the PFNA blade or lag screw. Through this way, the lag screw and helical blade get a good purchase that docked at femoral calcar. Therefore, the superior border of the tack hole can be used as presser to prevent the wire from deviating upward. When guide wire just passed the tack hole of the nail, the rod of nail was slightly tapped down further to allow the superior border of the tack hole to touch the guide wire. Here, we are presenting a surgical technique to direct the guide wire to right track. The guide wire would always bend and flow superiorly away from femoral calcar, and the lag screw and helical blade will follow the track and get into superior part of femoral head, not into femoral calcar. One of difficulties encountered in operation is insertion of the guide wire to femoral head. Cephalomedullary fixation, including proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) and gamma nail, is commonly used in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Intertrochanteric fracture is the most common hip fractures in elderly population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
